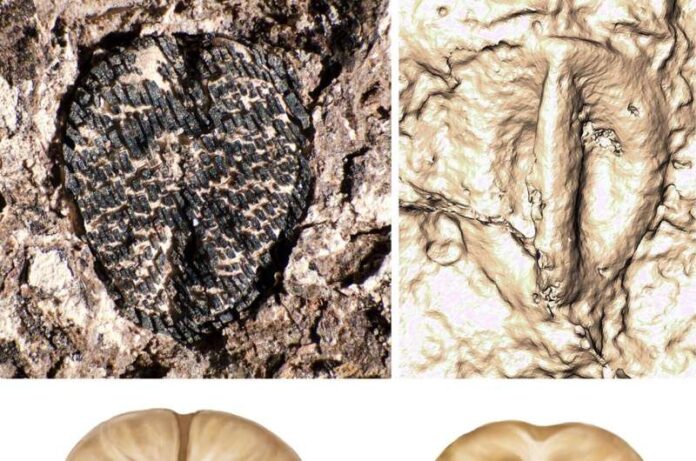
Paleontology, the study of ancient life through fossils, offers remarkable insights into the history of life on Earth. By examining fossilized remains, scientists have been able to piece together the evolution of species, uncovering extraordinary creatures that roamed the planet millions of years ago. From the discovery of massive dinosaurs to microscopic organisms, paleontology continues to shape our understanding of evolution, extinction, and the Earth’s ancient ecosystems. In this article, we will explore some of the most significant fossil discoveries, the ancient life forms they reveal, and how modern technology is revolutionizing paleontological research, driving new discoveries and expanding our knowledge of the distant past.
Let’s investigate this topic extensively with tirfblog.com
1. Introduction to Paleontology
Paleontology is the scientific study of ancient life through the examination of fossils, including the remains of plants, animals, and microorganisms that once inhabited Earth. This discipline bridges biology and geology, providing a window into the distant past and allowing us to explore how life has evolved over millions of years. Fossils, whether preserved bones, shells, imprints, or even traces like footprints, serve as crucial evidence in understanding extinct species and the environments they lived in.
Through paleontology, we gain valuable insights into mass extinctions, evolutionary patterns, and how different life forms adapted to changing climates and ecosystems. The field has evolved significantly since its inception, with early fossil discoveries sparking curiosity about life’s origins. Today, advanced techniques such as radiometric dating and DNA analysis enable paleontologists to make even more precise conclusions about ancient life.
By piecing together the fossil record, paleontology continues to expand our understanding of Earth’s history, helping to answer fundamental questions about the origin of species, adaptation, and survival over time.
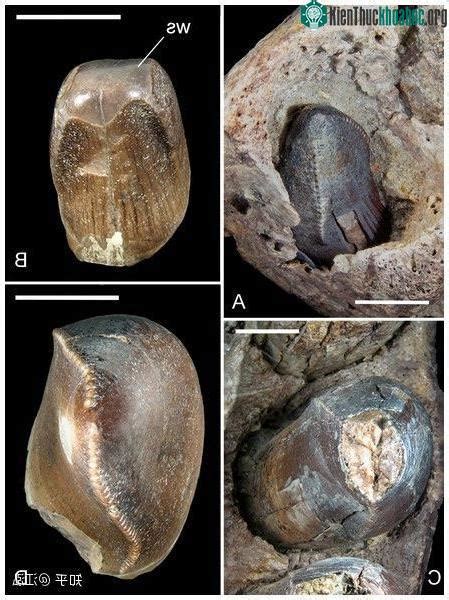
2. Significant Discoveries in Fossil Records
Throughout history, the fossil record has revealed extraordinary discoveries that have significantly advanced our understanding of life on Earth. One of the earliest and most groundbreaking finds was that of the Archaeopteryx in the 19th century, a feathered dinosaur that provided key evidence of the evolutionary link between reptiles and birds. Similarly, the discovery of the fossilized remains of Tyrannosaurus rex in the early 20th century showcased one of the most iconic predators from the Mesozoic era, offering deep insights into the behavior and physiology of large dinosaurs.
In more recent times, the unearthing of well-preserved woolly mammoth carcasses in Siberian permafrost has helped scientists study Ice Age megafauna in unprecedented detail. These findings have provided valuable information about how these massive creatures lived and their eventual extinction due to climatic changes. Additionally, discoveries like the Burgess Shale in Canada, a site rich in soft-bodied fossils, have expanded our knowledge of early marine life from over 500 million years ago.
Fossilized human ancestors, such as the famous “Lucy” Australopithecus afarensis skeleton, discovered in 1974, continue to reshape our understanding of human evolution. Each significant discovery within the fossil record adds a piece to the puzzle of life’s history, helping to fill gaps and refine theories about species development, adaptation, and extinction across different eras.
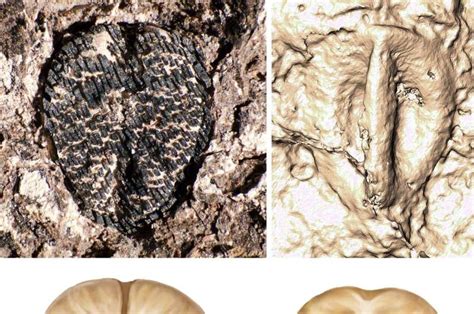
3. Ancient Life Forms: Key Species Unearthed
The fossil record has unearthed a wide variety of ancient life forms, each revealing critical details about Earth’s past ecosystems. Among the most famous discoveries is the trilobite, a marine arthropod that thrived during the Paleozoic era and is one of the earliest known complex life forms. Their widespread presence in fossil beds provides insight into early ocean ecosystems.
Dinosaurs, such as the plant-eating Brachiosaurus and the predatory Velociraptor, have long captured the public’s imagination. Their fossils have helped scientists understand the dominance of reptiles during the Mesozoic era, a time when vast herds of herbivores coexisted with fearsome predators.
The fossilized remains of early mammals like the small, rodent-like Morganucodon reveal the transition from reptilian to mammalian dominance after the dinosaurs’ extinction. Additionally, ancient marine reptiles like the plesiosaur and early birds like Confuciusornis further enrich our understanding of how different species adapted to their environments.
These key species provide a glimpse into the incredible diversity of life that once inhabited the planet.
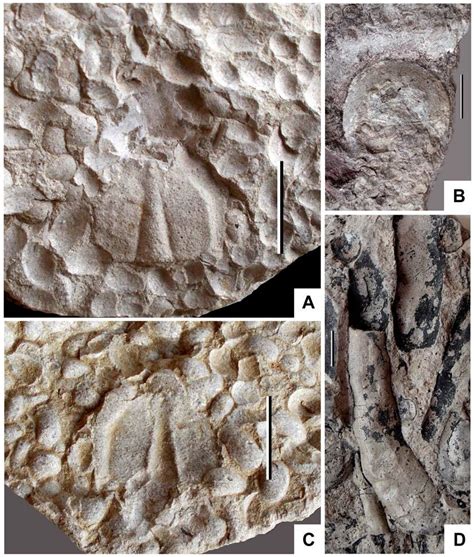
4. Impact of Discoveries on Evolutionary Theory
The discoveries within the fossil record have had a profound impact on the development of evolutionary theory. Charles Darwin’s theory of evolution by natural selection, introduced in On the Origin of Species, was supported by fossil evidence that demonstrated gradual changes in species over time. As more fossils were unearthed, such as transitional forms like Archaeopteryx and early hominids, the fossil record provided physical proof of species evolving and adapting to their environments.
These discoveries revealed that life on Earth is not static but constantly changing. The identification of extinct species highlighted the role of natural selection and environmental pressures in shaping life. Transitional fossils, like those linking reptiles and birds or fish and amphibians, bridged gaps in evolutionary history, providing direct evidence of species adaptation.
Furthermore, the study of ancient life forms and mass extinction events, such as the one that wiped out the dinosaurs, helped refine our understanding of the factors driving evolution. Fossil discoveries continue to validate and expand upon Darwin’s foundational ideas, shaping modern evolutionary science.
5. Technological Advances in Paleontological Research
Technological advances have revolutionized paleontological research, allowing scientists to explore ancient life with unprecedented precision. One of the most significant developments is the use of CT scanning, which enables researchers to create detailed 3D models of fossils without damaging them. This technology has been instrumental in examining the internal structures of bones and even delicate fossils, revealing new insights into how ancient species lived and moved.
Another major advancement is the application of radiometric dating techniques, which allow paleontologists to determine the age of fossils with great accuracy. This has helped create a more precise timeline of Earth’s history, placing significant discoveries in their correct chronological context.
Additionally, advances in DNA extraction techniques have allowed scientists to analyze genetic material from well-preserved fossils, such as woolly mammoths, offering clues about their evolutionary relationships and adaptations. The use of drones and satellite imagery has also improved fieldwork efficiency, helping to locate fossil sites in remote areas, expanding the potential for new discoveries.
6. Notable Paleontologists and Their Contributions
The field of paleontology has been shaped by the contributions of many notable scientists whose discoveries have advanced our understanding of ancient life. One of the most famous figures is Mary Anning, a self-taught paleontologist from the early 19th century. Her discoveries along England’s Jurassic Coast, including the first complete Ichthyosaurus skeleton, provided critical evidence for understanding marine reptiles and early life forms.
Charles Doolittle Walcott made a groundbreaking discovery in 1909 when he unearthed the Burgess Shale in Canada, a fossil-rich deposit containing well-preserved soft-bodied organisms from the Cambrian period. This site has become one of the most important windows into early marine ecosystems.
In more recent times, Jack Horner’s work on dinosaur fossils, particularly his studies on Maiasaura, has provided insight into dinosaur parenting and social behavior, challenging previous assumptions about these prehistoric creatures. Horner also contributed to the theory that birds are the direct descendants of dinosaurs.
Richard Leakey, a prominent paleoanthropologist, has made crucial contributions to the study of early human ancestors. His work in East Africa, particularly the discovery of nearly complete hominid fossils, has reshaped our understanding of human evolution.
These paleontologists, along with many others, have expanded the scope of paleontology, uncovering critical links between extinct species and the evolutionary history of life on Earth.
7. Future Directions and Ongoing Research in Paleontology
The future of paleontology is poised for exciting developments as researchers continue to push the boundaries of science and technology. One of the most promising areas is the use of advanced imaging techniques, such as synchrotron radiation and high-resolution CT scans, which allow scientists to explore fossilized remains in unprecedented detail. These technologies will enable the examination of previously inaccessible features, offering deeper insights into the biology and behavior of ancient organisms.
Additionally, the application of genetic analysis is expected to advance further, with researchers extracting and sequencing DNA from increasingly older and more degraded fossils. This could provide new information about the evolutionary relationships between species and their adaptations to past environments.
Ongoing research into mass extinction events and their causes is another crucial area of focus. Understanding these events will help scientists predict how current climate changes might impact modern species.
Fieldwork will also expand into new and previously unexplored regions, potentially uncovering new fossils that could fill gaps in the evolutionary record. Collaborative international projects and interdisciplinary approaches, combining paleontology with geology, ecology, and genetics, will enhance our understanding of ancient life and its connections to modern ecosystems.
Paleontology continues to unveil the mysteries of ancient life, offering profound insights into the history of our planet. From groundbreaking fossil discoveries to technological advancements and the contributions of pioneering scientists, this field has significantly enhanced our understanding of evolution and Earth’s past ecosystems. As new technologies and research methods emerge, paleontologists are poised to make even more discoveries that will further illuminate the intricate tapestry of life’s history and its impact on the present.
tirfblog.com