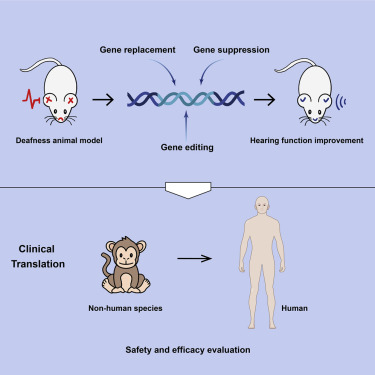
Gene therapy represents a revolutionary approach to treating genetic disorders by directly addressing the underlying genetic causes rather than merely managing symptoms. As advancements in genetic research and biotechnology accelerate, gene therapy has evolved from a theoretical concept to a viable treatment option, offering hope to patients with conditions once considered untreatable. Recent breakthroughs have demonstrated the potential of gene therapy to correct defective genes, providing lasting solutions for disorders such as cystic fibrosis, muscular dystrophy, and certain types of cancer. This article explores the latest advancements in gene therapy, highlights the key disorders targeted, and discusses the future potential and challenges of this transformative field.
Let’s explore this topic in detail with tirfblog.com
1. Introduction to Gene Therapy: Definition and Importance
Gene therapy is an innovative medical technique that involves altering genes within an individual’s cells to treat or prevent disease. Unlike traditional treatments that often focus on alleviating symptoms, gene therapy aims to correct the underlying genetic issues that cause disorders. This can involve replacing a faulty gene with a healthy one, inactivating a malfunctioning gene, or introducing a new gene to help fight a disease. The importance of gene therapy lies in its potential to provide long-term, and sometimes permanent, solutions for a wide range of genetic disorders, many of which currently have limited or no effective treatments.
The significance of gene therapy extends beyond just treating rare genetic diseases; it also has implications for more common conditions, such as cancer, heart disease, and neurological disorders. By targeting the root cause at the genetic level, gene therapy opens up new avenues for personalized medicine, where treatments are tailored to the unique genetic makeup of individuals. As research continues to advance, gene therapy stands poised to revolutionize the future of healthcare, offering hope to millions worldwide.
2. Recent Breakthroughs in Gene Therapy Techniques
Recent breakthroughs in gene therapy have significantly advanced the field, making it a more viable and effective treatment option for various genetic disorders. One of the most notable innovations is the development of CRISPR-Cas9, a gene-editing technology that allows precise modifications to DNA with unprecedented accuracy. This technique has revolutionized gene therapy by enabling scientists to target and correct specific genetic mutations at their source. Additionally, advancements in viral vector technology have improved the delivery of therapeutic genes into patients’ cells, increasing the safety and efficiency of treatments.
Another major breakthrough is the use of gene therapy in vivo, where genes are delivered directly into the body, allowing for more targeted and effective treatments. This has shown promising results in treating conditions such as spinal muscular atrophy and inherited retinal diseases. These advancements not only expand the range of disorders that can be treated but also enhance the potential for more personalized and precise medical interventions, offering new hope for patients with previously untreatable conditions.
3. Key Genetic Disorders Targeted by Gene Therapy
Gene therapy has shown promise in treating a range of genetic disorders by addressing the root cause at the molecular level. One of the key targets is cystic fibrosis, a life-threatening disorder caused by mutations in the CFTR gene, leading to severe respiratory and digestive problems. By correcting or replacing the faulty gene, gene therapy offers a potential long-term solution to improve patients’ quality of life.
Another major target is hemophilia, a blood-clotting disorder caused by mutations in the genes responsible for producing clotting factors. Gene therapy aims to introduce functional versions of these genes, potentially providing a cure that eliminates the need for regular clotting factor infusions. Inherited retinal diseases, such as Leber congenital amaurosis, have also been successfully treated with gene therapy, restoring vision in patients who were previously facing blindness.
Spinal muscular atrophy (SMA), a severe genetic disorder affecting motor function, has seen breakthroughs with gene therapy treatments that replace the defective SMN1 gene, significantly improving motor skills and survival rates in affected children. These advancements underscore gene therapy’s potential to transform the treatment landscape for various genetic disorders.
4. Case Studies: Successful Gene Therapy Treatments
Case studies of successful gene therapy treatments illustrate the transformative potential of this approach. One prominent example is the treatment of spinal muscular atrophy (SMA), a genetic disorder that causes severe muscle weakness. The introduction of Zolgensma, a gene therapy that replaces the defective SMN1 gene, has led to remarkable improvements in motor function and survival rates. Infants treated with Zolgensma have demonstrated significant developmental gains, often reaching milestones that were previously unattainable.
In another notable case, Luxturna, a gene therapy for inherited retinal diseases such as Leber congenital amaurosis, has restored vision in patients with severe retinal degeneration. By delivering a healthy copy of the RPE65 gene directly to the retinal cells, Luxturna has enabled individuals to regain functional vision, significantly enhancing their quality of life.
The success of these treatments underscores the potential of gene therapy to provide long-term, impactful solutions for genetic disorders. These case studies not only highlight the effectiveness of gene therapy in addressing specific genetic defects but also offer hope for the future of personalized medicine, where targeted therapies could transform the treatment landscape for a wide range of genetic conditions.
5. Ethical Considerations in Gene Therapy
The advancement of gene therapy raises several ethical considerations that must be carefully addressed. One major concern is the potential for unintended genetic changes or off-target effects. While technologies like CRISPR-Cas9 have enhanced precision, the possibility of altering unintended genes remains a significant issue, potentially leading to unforeseen health consequences.
Another ethical challenge is the accessibility and equity of gene therapy. These advanced treatments are often expensive and may not be available to all patients who could benefit from them. This disparity raises concerns about fairness and the potential widening of existing health inequalities, as only a select few may have access to these life-saving therapies.
Additionally, the concept of germline gene therapy, which involves modifying genes in embryos or reproductive cells, poses profound ethical questions. Such modifications could be passed on to future generations, raising concerns about long-term effects and the potential for creating genetic “designer babies,” where genetic traits could be selected for non-medical reasons.
Ethical considerations also include the potential psychological impact on patients and families undergoing gene therapy. The high expectations and emotional burden associated with these treatments must be managed carefully, ensuring that patients are fully informed and supported throughout their treatment journey. Addressing these ethical concerns is crucial for the responsible advancement of gene therapy and its integration into mainstream medicine.
6. Future Prospects and Research Directions in Gene Therapy
The future of gene therapy holds exciting prospects and numerous research directions aimed at expanding its applications and improving outcomes. One promising area is the development of more precise and efficient gene-editing technologies. Advances in tools like CRISPR-Cas9, along with new methods such as base editing and prime editing, aim to enhance accuracy and minimize off-target effects, making gene therapy safer and more effective.
Research is also focused on improving gene delivery systems. Current methods often rely on viral vectors, but new strategies, including non-viral delivery techniques and engineered nanoparticles, are being explored to enhance the delivery of therapeutic genes and reduce potential risks associated with viral vectors.
Additionally, expanding the range of treatable genetic disorders is a key research direction. Scientists are working on applying gene therapy to complex diseases with multiple genetic components, such as cancer and neurodegenerative disorders, potentially offering novel treatments where traditional methods have been limited.
Personalized gene therapy, tailored to individual genetic profiles, is another exciting avenue. Advances in genomics and bioinformatics will enable more precise targeting of gene therapies to address unique genetic mutations in patients.
Overall, continued innovation and research in gene therapy promise to revolutionize the treatment of genetic disorders, offering new hope and potential cures for a wide array of conditions.
7. Challenges and Limitations of Current Gene Therapy Methods
Despite the significant advancements in gene therapy, several challenges and limitations persist. One major challenge is the risk of off-target effects, where gene-editing tools like CRISPR-Cas9 might inadvertently alter unintended parts of the genome, potentially leading to harmful outcomes. Ensuring precision and safety remains a critical focus.
Another limitation is the difficulty in effectively delivering therapeutic genes to the appropriate cells. Current methods, particularly viral vectors, can be associated with immune responses and other complications. Developing more efficient and safer delivery systems is essential to overcoming this barrier.
Additionally, the high cost of gene therapy treatments poses a significant challenge, limiting accessibility for many patients. The expense of developing, manufacturing, and administering these therapies can restrict their availability to a broader population.
Lastly, there are concerns about the long-term effects and durability of gene therapies. Ensuring that treatments provide lasting benefits without adverse long-term consequences is crucial for their overall success and acceptance in the medical community.
8. Impact of Gene Therapy on Healthcare and Society
Gene therapy has the potential to significantly impact both healthcare and society by transforming the treatment landscape for genetic disorders. By addressing the root causes of diseases rather than just managing symptoms, gene therapy offers the possibility of long-term or even permanent cures, potentially reducing the burden on patients and healthcare systems. This shift towards more effective treatments could lead to substantial improvements in quality of life and health outcomes.
On a societal level, the widespread adoption of gene therapy could change perceptions of genetic disorders, shifting them from being seen as chronic, untreatable conditions to manageable or curable diseases. This could foster greater hope and optimism among affected individuals and their families.
However, the high cost and limited accessibility of current gene therapies could exacerbate healthcare disparities, making it essential to address these issues to ensure equitable access. Overall, as gene therapy continues to advance, its impact on healthcare and society will likely be profound, driving progress towards more personalized and effective medical care.
Gene therapy represents a groundbreaking advancement in medicine, offering the potential to cure genetic disorders by addressing their root causes. While significant progress has been made with successful treatments and innovative techniques, challenges such as precision, accessibility, and cost remain. As research continues to evolve, gene therapy holds promise for transforming healthcare and improving lives on a global scale.
tirfblog.com