Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) is a mental health condition triggered by experiencing or witnessing a traumatic event. It can affect anyone, from military personnel to survivors of accidents, abuse, or natural disasters. The lingering effects of PTSD can disrupt daily life, relationships, and overall well-being. Understanding the causes and psychological impact of PTSD is crucial for recognizing symptoms and seeking timely help. This article explores the common causes of PTSD, its psychological toll, and offers effective coping strategies, including both psychological approaches and lifestyle adjustments. Additionally, it highlights the importance of support systems and community resources for better mental health.
Let’s explore this topic in detail with tirfblog.com
1. Introduction to PTSD
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) is a complex mental health condition that emerges following exposure to traumatic events, including combat, natural disasters, serious accidents, or personal assaults. These events can leave lasting emotional scars, and for some individuals, the psychological effects persist long after the initial trauma has passed. PTSD not only impacts the individual who experienced the trauma but can also significantly affect their relationships, work, and overall daily functioning.
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is characterized by a range of distressing symptoms, including intrusive thoughts, nightmares, flashbacks, and intense anxiety. These symptoms can significantly impact an individual’s ability to function, hindering their progress in life. PTSD is not confined to any particular group; it can affect individuals of all ages and backgrounds. However, certain populations, such as military veterans or survivors of abuse, may have a higher likelihood of experiencing this disorder.
The journey to healing from PTSD begins with understanding the condition. Recognizing the signs and seeking professional help are crucial first steps. This article aims to be a comprehensive guide, exploring the causes, psychological effects, and coping strategies for PTSD. It will equip individuals with the knowledge needed to navigate and manage this challenging condition.
2. Common Causes of PTSD
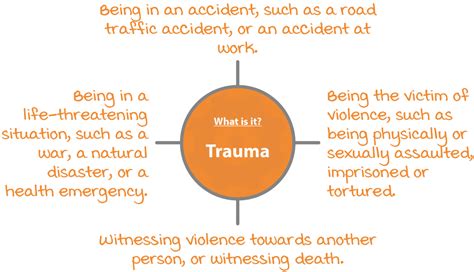
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) can emerge following a traumatic event that endangers an individual’s life or well-being, whether they directly experience it or witness it. While combat and military service are commonly linked to PTSD, the condition can arise from a multitude of other sources. Individuals who have survived physical or sexual assault, domestic violence, or childhood abuse face a heightened risk of developing PTSD. Additionally, natural disasters, such as earthquakes or hurricanes, can trigger PTSD, as can accidents like car crashes or plane crashes.
Trauma isn’t always a direct experience. Witnessing violence, the sudden loss of a loved one, or even being in a life-threatening situation can all trigger Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD). The severity and length of the traumatic event, along with an individual’s resilience and the support they receive, can determine whether or not they develop PTSD.
While not everyone exposed to trauma develops PTSD, understanding its common causes is crucial for recognizing potential triggers and encouraging those affected to seek support. Early intervention plays a vital role in preventing long-term psychological consequences and promoting recovery. Raising awareness about the origins of PTSD is therefore key to addressing this debilitating condition.
3. Psychological Impact of PTSD
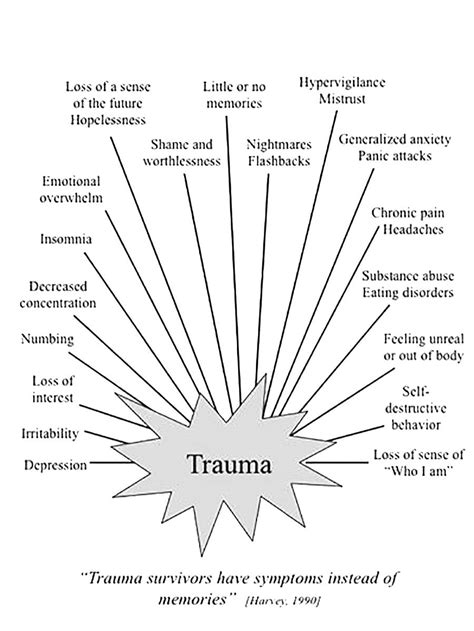
The psychological consequences of PTSD are far-reaching, permeating every facet of an individual’s life. Sufferers frequently contend with intrusive thoughts or flashbacks, reliving the traumatic event as if it were occurring in the present moment. These intrusive memories can be triggered by seemingly unrelated stimuli, including sounds, smells, or locations, leading to intense emotional and physical responses.
People with PTSD often experience anxiety and hypervigilance, leaving them feeling constantly afraid or on edge. This heightened state of alertness makes it hard to relax, contributing to sleep problems like insomnia or frequent nightmares. These symptoms can have a long-term impact, leading to depression, social withdrawal, and a sense of hopelessness.
PTSD can significantly damage self-esteem and confidence, hindering daily activities and straining relationships. The condition often manifests in irritability, anger outbursts, and impaired concentration, further disrupting work and social interactions. Some individuals may resort to unhealthy coping mechanisms, like substance abuse, to alleviate the emotional distress.
The profound psychological impact of PTSD highlights the critical need for prompt diagnosis and intervention. By addressing symptoms through therapy, supportive care, and effective coping strategies, individuals can minimize long-term consequences and embark on a path towards healing.
4. Diagnosis and Seeking Help
Diagnosing PTSD involves a comprehensive assessment by a mental health professional. Symptoms must persist for more than a month and significantly interfere with daily life for a diagnosis to be made. The process typically includes a detailed discussion of the traumatic event, the symptoms experienced, and their impact on the individual’s functioning. PTSD can sometimes be misdiagnosed as depression or anxiety, making it essential for individuals to seek help from a specialist familiar with trauma-related disorders.
Seeking help early is crucial in managing PTSD. Treatment options include psychotherapy, such as Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) or Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR), both of which are effective in addressing trauma. Medications, such as antidepressants, may also be prescribed to alleviate symptoms like anxiety and depression.
Support from family, friends, and community resources plays a vital role in the recovery process. Encouraging those affected to reach out and seek professional help can make a significant difference in their journey toward healing, reducing the long-term psychological effects of PTSD.
5. Coping Strategies: Psychological Approaches
Psychological approaches play a crucial role in assisting individuals with PTSD in managing their symptoms and enhancing their quality of life. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) stands out as one of the most effective treatments, aiming to modify negative thought patterns and behaviors linked to trauma. CBT empowers individuals to challenge and reframe distorted beliefs, leading to a gradual reduction in symptom intensity. Exposure Therapy, another potent method, involves the gradual exposure of individuals to memories or situations connected to the trauma within a controlled setting. This process helps diminish fear and avoidance behaviors, enabling them to regain control over their lives.
Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR) is another widely recognized approach in psychology. This therapy utilizes guided eye movements to help the brain process and integrate traumatic memories, lessening their emotional impact. EMDR can be especially helpful for individuals who find it difficult to directly discuss their trauma.
Beyond traditional therapies, mindfulness-based practices can also be beneficial. By cultivating present moment awareness, these techniques help individuals manage anxiety and reduce intrusive thoughts. These psychological methods offer a structured framework for healing, empowering individuals with PTSD to confront and process their trauma in a safe and supportive environment. This ultimately contributes to long-term recovery.
6. Coping Strategies: Lifestyle Adjustments
Lifestyle changes can be a vital part of managing PTSD, working alongside traditional psychological therapies. Establishing a consistent daily routine provides structure and stability, helping to reduce anxiety and create a sense of normalcy in daily life. Regular exercise is particularly helpful, as physical activity releases endorphins, which improve mood and reduce stress. Activities such as yoga, walking, or swimming can also promote relaxation and mindfulness.
Your diet can also affect your mental health. Eating a balanced diet with plenty of fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains can help your brain work better and improve your emotional well-being. It’s also important to avoid too much caffeine and alcohol, as these can make anxiety worse and disrupt your sleep.
Sleep hygiene is a crucial aspect of lifestyle change. Implementing a relaxing bedtime routine, adhering to a consistent sleep schedule, and creating a comfortable sleep environment can alleviate insomnia and enhance overall mental well-being. Moreover, exploring healthy stress management techniques, such as engaging in hobbies, journaling, or meditation, can provide emotional solace and prevent the escalation of symptoms.
Having a robust support network is essential for success. Connecting with friends, family, or support groups provides emotional support and combats feelings of isolation, making these lifestyle changes an integral part of managing PTSD.
7. Support Systems and Community Resources
Support systems and community resources are crucial for individuals coping with PTSD, providing emotional support and practical assistance. Connecting with family and friends can offer a sense of understanding and reduce feelings of isolation. Encouraging open communication and fostering supportive relationships help individuals feel less alone in their journey toward recovery.
Community resources such as support groups and counseling services offer additional avenues for help. Support groups, often facilitated by mental health professionals or peer leaders, provide a space for sharing experiences and strategies for coping with PTSD. These groups can also offer a sense of community and validation, which is essential for healing.
Nonprofit organizations and community health centers frequently offer resources tailored to PTSD, including workshops, educational materials, and crisis intervention services. Online resources, such as forums and helplines, can also provide valuable information and support, especially for those who may not have access to in-person services.
Veterans’ organizations and specialized PTSD programs may offer targeted support for individuals who have experienced combat or military-related trauma. Leveraging these resources can greatly enhance recovery, helping individuals build a strong support network and access the help they need to manage PTSD effectively.
Understanding PTSD, its causes, and its psychological impact is vital for effective management and recovery. By combining psychological approaches with lifestyle adjustments and leveraging support systems, individuals can better cope with the disorder. Early intervention and ongoing support play crucial roles in improving mental health and helping those affected lead fulfilling lives.
tirfblog.com

